Automotive Electronics Thermal Solution
-
Solution Overview
Automotive electronics are becoming increasingly complex and compact, which means that heat dissipation is a critical factor in their design. The thermal solution for automotive electronics involves the use of various thermal management technologies to maintain the optimal operating temperature of electronic components. Thermal interface materials (TIMs) are a critical component of the thermal solution for automotive electronics. They are used to improve the thermal contact between electronic components and heat sinks, which helps to dissipate heat and maintain the optimal operating temperature of the components.
Thermal interface materials (TIMs): TIMs are used to improve the thermal contact between electronic components and heat sinks. They are typically made of a thermally conductive material, such as grease or a phase change material. There are several different types of TIMs available, including thermal greases, thermal pads, and phase change materials. Each type of TIM has its own unique properties and advantages.
Thermal greases are the most common type of TIM used in automotive electronics. They are made of a thermally conductive material, such as silicone or zinc oxide, and are designed to fill the microscopic gaps between the electronic component and the heat sink. This helps to improve the thermal contact between the two surfaces, which in turn improves heat transfer.
Thermal pads are another type of TIM that are commonly used in automotive electronics. They are made of a thermally conductive material, such as silicone or graphite, and are designed to provide a cushion between the electronic component and the heat sink. This helps to absorb any imperfections in the two surfaces, which in turn helps to improve thermal contact. Phase-change materials are a third type of TIM that are sometimes used in automotive electronics. They are designed to change phase from solid to liquid when they reach a certain temperature. This helps to fill any gaps between the electronic component and the heat sink, which in turn improves thermal contact.
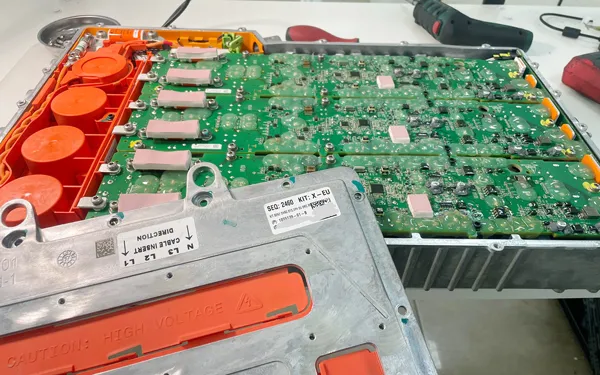
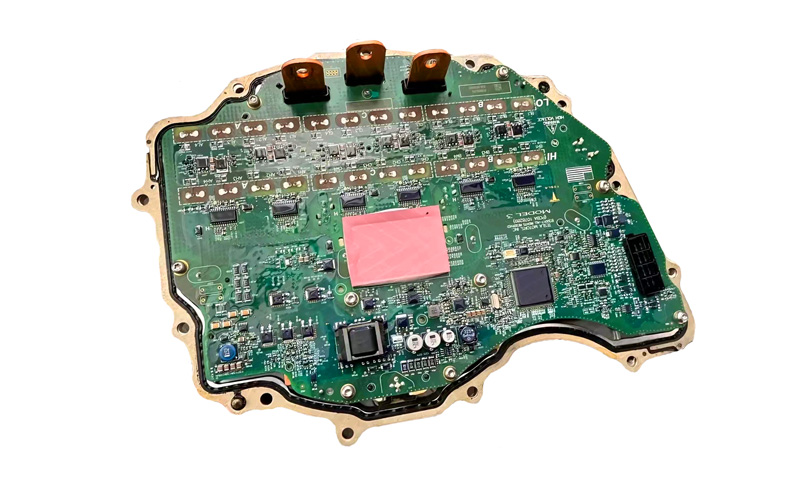
Tesla Onboard Charger(OBC)
Tesla Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
The functions of thermal interface materials (TIMs) for automotive electronics include:
Heat dissipation: Automotive electronic devices generate heat during operation. If the heat is not dissipated in a timely manner, it can lead to device damage or performance degradation. TIMs can transfer the heat generated by electronic devices to heat sinks or other cooling components for rapid heat dissipation, keeping the devices at a normal operating temperature.
Improving heat transfer efficiency: TIMs can fill the gaps between electronic devices and heat sinks, reducing thermal resistance and uneven heat transfer, improving heat transfer efficiency, preventing local overheating, and reducing device failure rates.
Preventing excessive temperature of electronic components: Excessive temperature can affect the performance and lifespan of electronic components, leading to equipment failure. TIMs can effectively control the temperature of electronic components, keeping them within a safe range and extending the lifespan of devices.
Reducing noise: High temperature and overheating can cause electronic devices to generate noise, affecting the driving experience. TIMs can effectively control the temperature, reduce noise, and improve riding comfort.
In summary, TIMs are essential for automotive electronics, improving the performance and reliability of electronic devices, protecting them from overheating damage, and extending their lifespan.
-
Solution