Datacom Thermal Solution
-
Solution Overview
The smart router is based on an open system and supports application installation, such as network acceleration, overturning the wall, advertising filtering, NFC, etc. Some smart routers are also equipped with large-capacity hard drives or support external SD cards, which can be used as storage devices. In short, the smart router has become a small computer. With the increase of product functions, the heat dissipation of the device will become a very severe test for engineers (increased heating components, increased power consumption, and compact structure). The requirements for thermal conductivity materials will also increase. The more diverse.
The role of thermal conductive materials in data communication equipment is to quickly transfer the heat generated inside the equipment to the outside to achieve the purpose of heat dissipation. A certain amount of heat will be generated inside the data communication equipment. If the heat cannot be dissipated in time, it will affect the performance and life of the equipment.
Thermally conductive material is a material with high thermal conductivity, such as heat dissipation glue or heat dissipation pad. These materials can effectively transfer heat to the device casing, and then release the heat to the outside through ways such as heat sinks or cooling holes on the casing.
In the design and manufacture of data communication equipment, the selection and application of thermally conductive materials are very important. The better the thermal conductivity of the thermally conductive material, the faster the heat inside the device can be transferred to the outside, thereby improving the heat dissipation effect of the device. In addition, the reliability, stability and safety of thermally conductive materials are also factors that need to be considered.
Therefore, thermally conductive materials play an important role in data communication equipment, which can help the equipment to dissipate heat better and ensure the performance and life of the equipment. At the same time, equipment designers should fully consider the heat dissipation problem when designing, and use casings and heat sinks with reasonable heat dissipation design to increase the heat dissipation area to ensure that the equipment can quickly dissipate heat.
-
Solution
Netcom product types
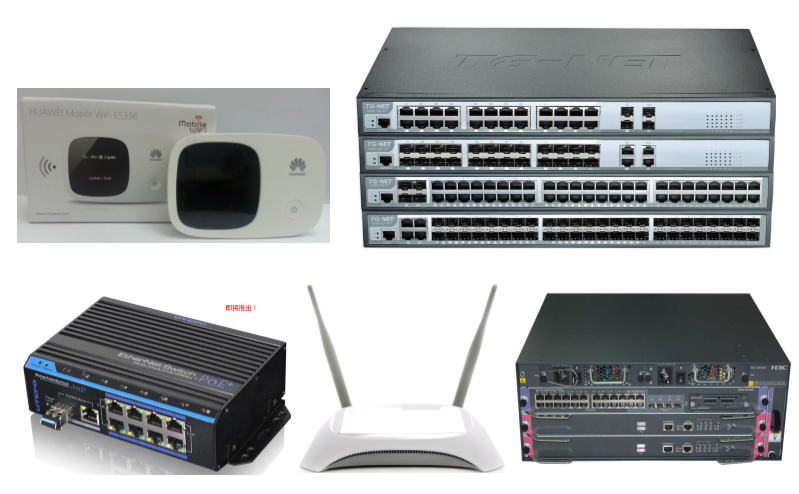


Product Model Details
Product model detail diagram
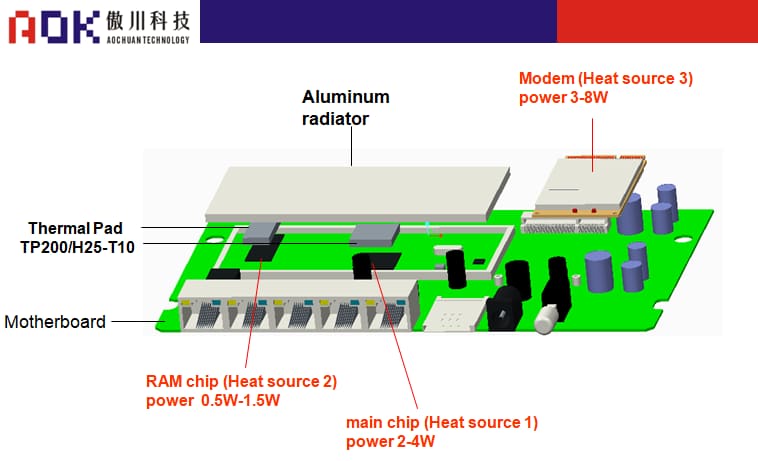
Schematic diagram of wireless router structure
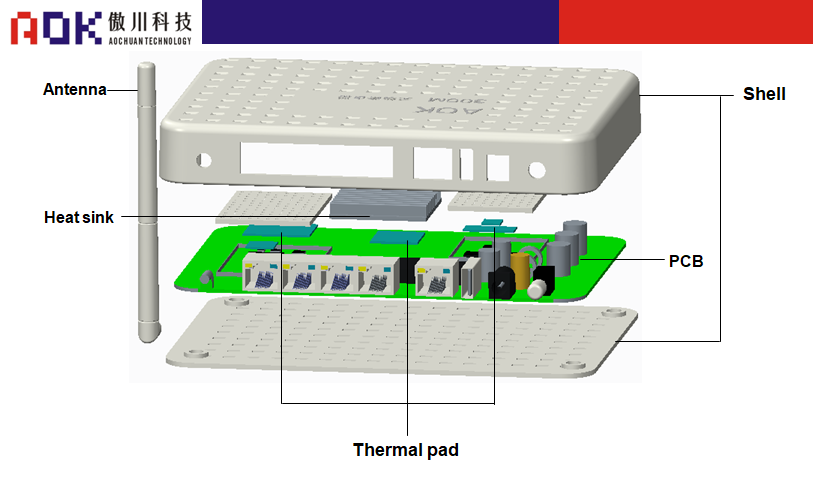
Schematic diagram of wireless router structure
1
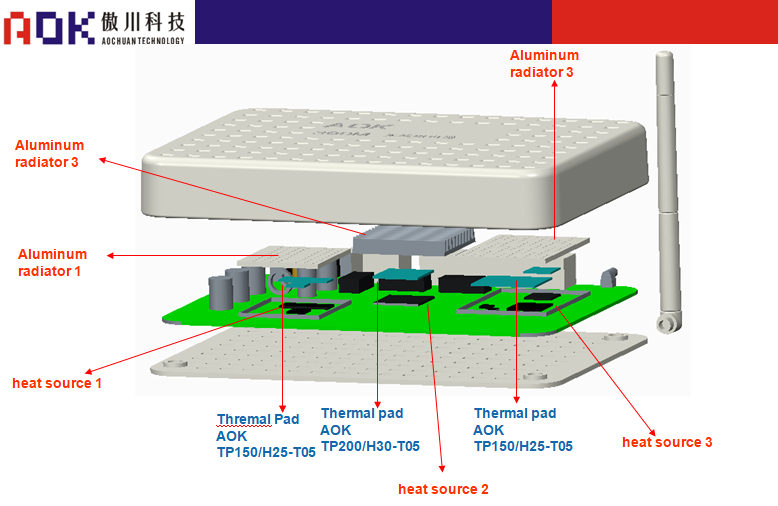
2
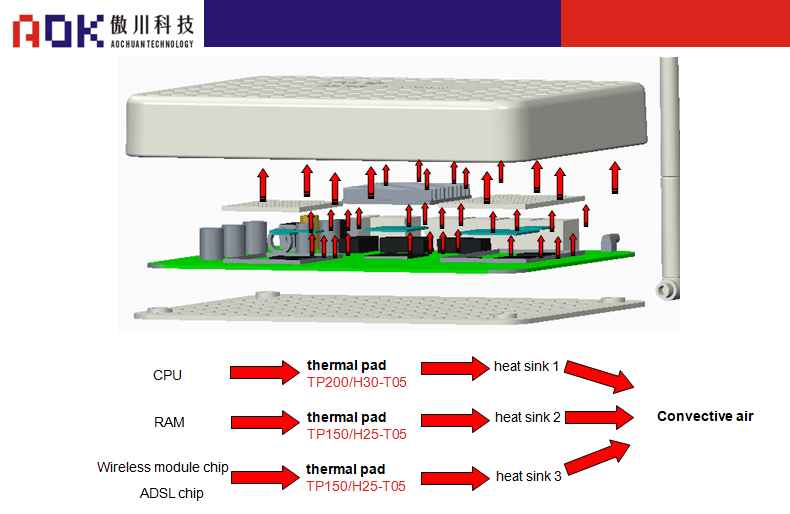
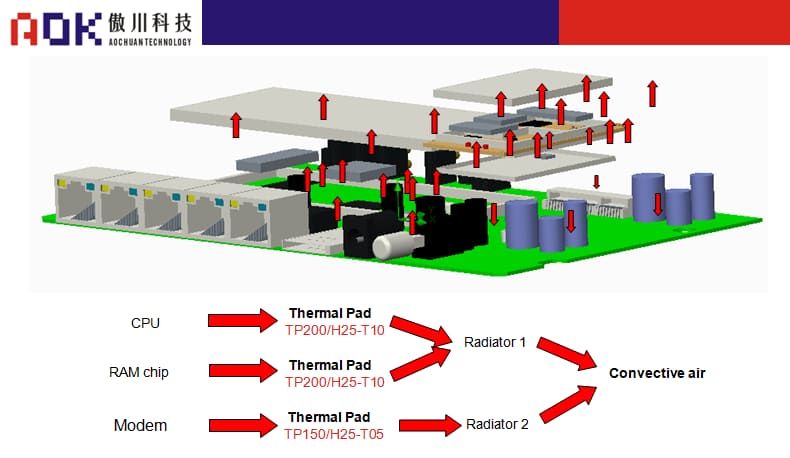
Schematic diagram of shell heat conduction
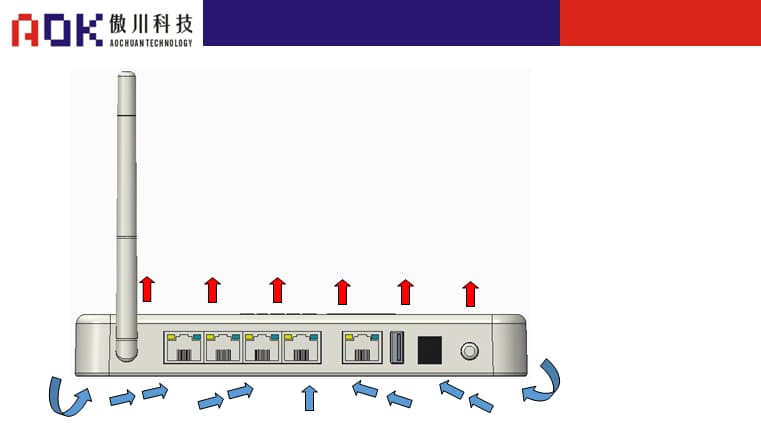
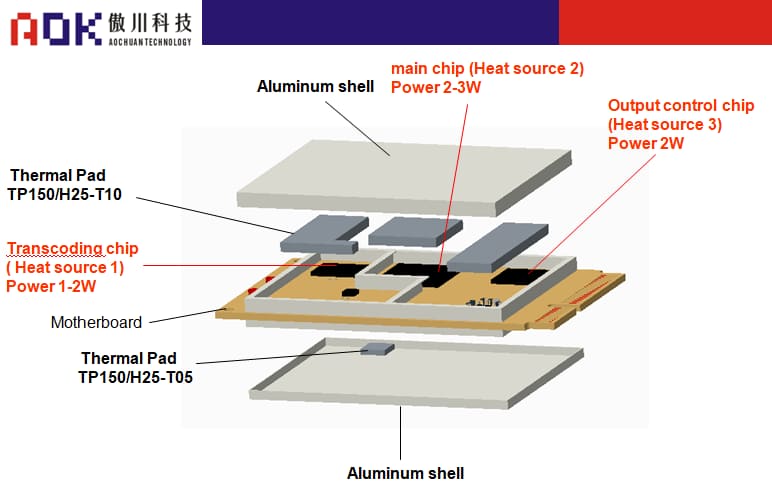
Internal structure diagram of portable WLAN equipment
Modem internal structure diagram
Schematic diagram of temperature rise
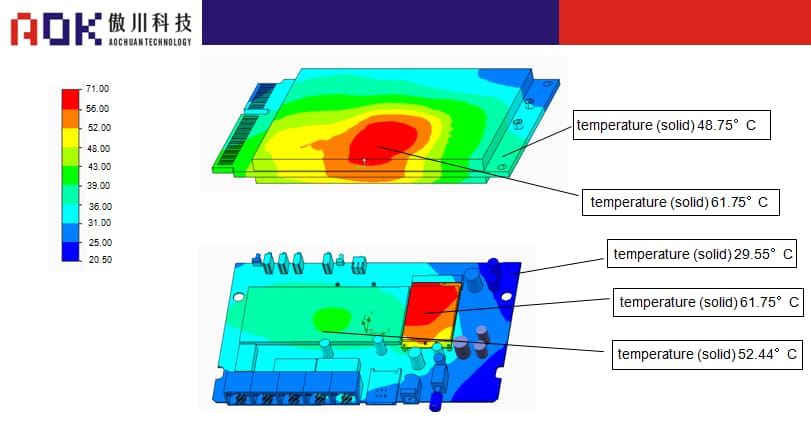
Router temperature rise :
Indoor: The test surface temperature does not exceed 60°C in full load operation at ambient temperature; the CPU temperature does not exceed 80°C; over-temperature and frequency reduction.
Outdoor: Test the surface temperature of 70°C-80°C under full load at ambient temperature; the maximum temperature of CPU is 110-120°C, over-temperature frequency reduction
Portable WLAN temperature rise: running at full load at room temperature, the surface temperature of the device does not exceed 55°C, the CPU temperature does not exceed 65°C, and the frequency is over-temperature reduced.
Portable WLAN
Product application scenarios
Product application scenarios
Main heating chip power and thermal interface material selection-thermal pad
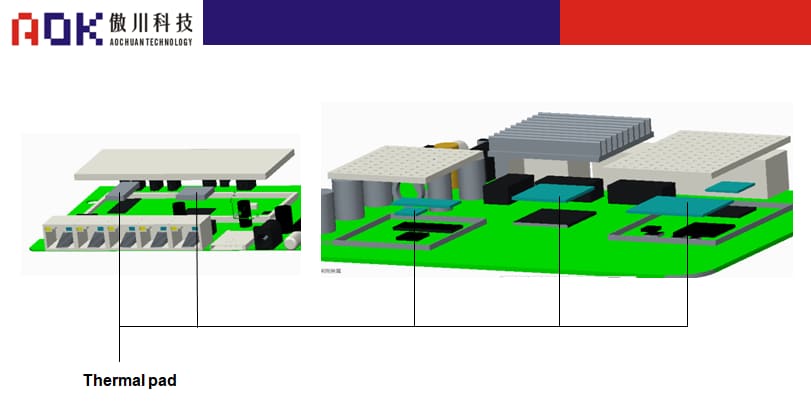
Heat source power Materials used Usage special requirements 1-2W/3-5W thermal pad
Thermal Conductivity:1.2-2.5w/m.k
Thickness:0.25-1.0mm
Breakdown Voltage:6kvFill the gap between the CPU, ADSL, wireless module and the aluminum radiator, transfer the chip heat to the radiator, and play the role of heat conduction and shock absorption. Because routers/portable WLANs involve high-frequency emission sources such as wireless transmitting antennas, the requirements for gaskets must not affect electromagnetic waves. Main heating chip power and thermal interface material selection-thermal pad
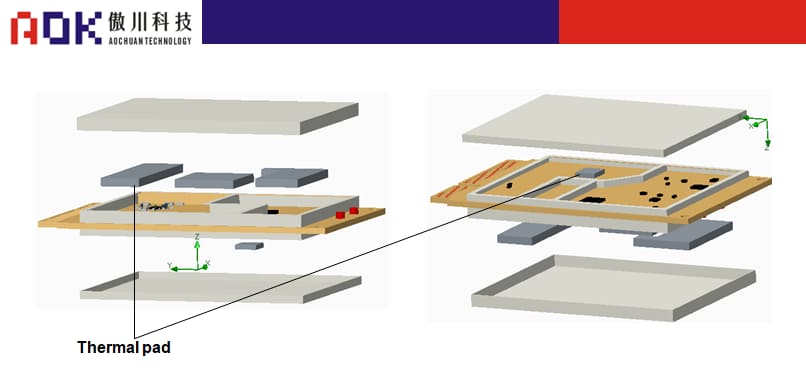
Heat source power Materials used Usage special requirements 2-4W thermal pad
Thermal Conductivity : 1.5-2.5w/m.k
Thickness:0.5-1.0mm
Breakdown Voltage:6kvThermal conduction, filling and shock absorption between the internal decoding chip, main chip and output control IC of the Modem module and the aluminum radiator. Because routers/portable WLANs involve high-frequency emission sources such as wireless transmitting antennas, the requirements for gaskets must not affect electromagnetic waves. Other router structures
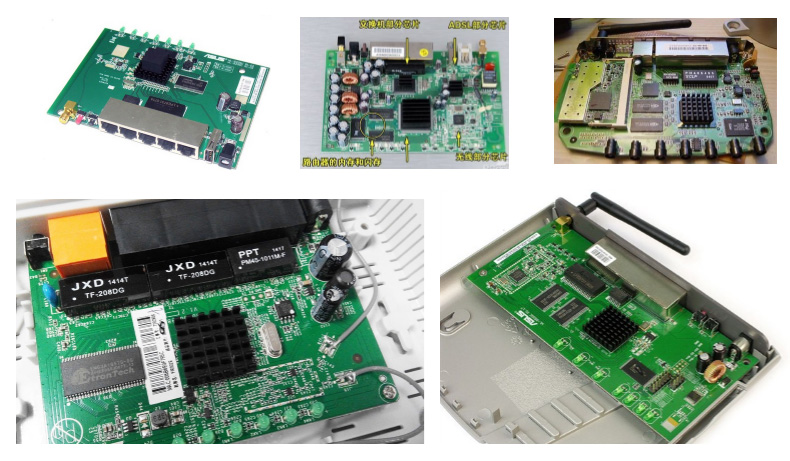

Other router structures

Schematic diagram of switch structure
1
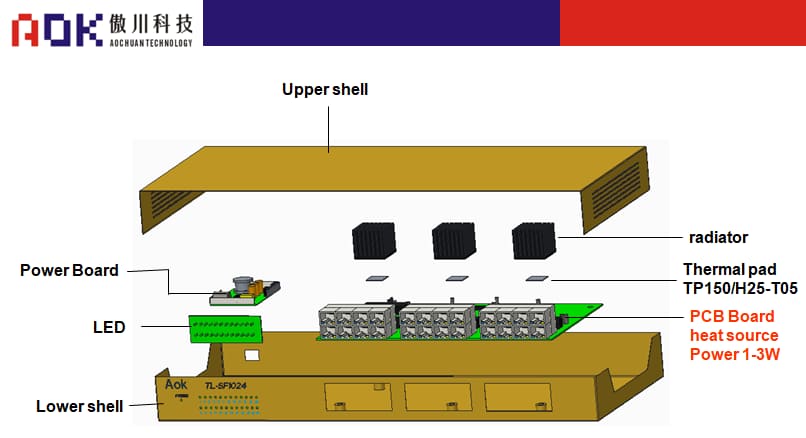
2
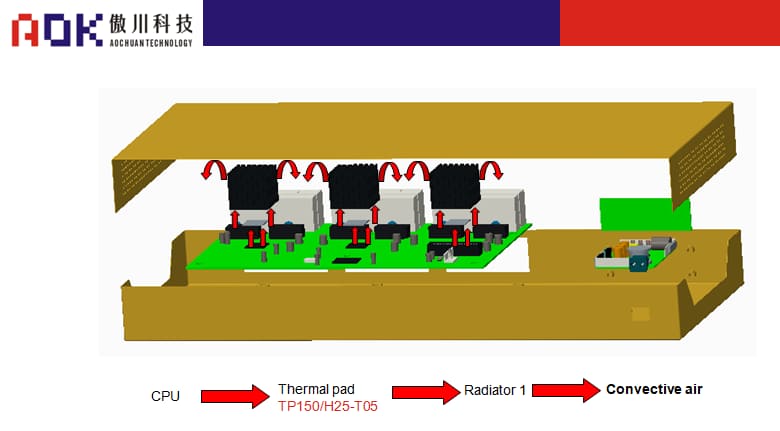
Heat source power Materials used Usage 1-2W/3-5W thermal pad
Thermal Conductivity:1.0-1.5w/m.k
Thickness:0.25-1.0mm
Breakdown Voltage:6kvFill the gap between the CPU, ADSL, wireless module and the aluminum radiator, transfer the chip heat to the radiator, and play the role of heat conduction and shock absorption.

