What Is a Thermal Interface Material Conductivity?
- Posted on:2023-03-14 10:43:00
- Source:AOK Thermal Pad Manufacturer FAQs
For the case of one-dimensional heat-flow, thermal conductivity (K) is defined as follows (fourier's law)
Equation: K = q • t / A • △T
where: q = heat flow (or power) in Watts
t = length of heat path (i.e., interface thickness) in meters
A = area in meters
△T = temperature difference across the interface, in degree C
Thermal conductivity is often expressed in reduced units of W/m.K or "Watts permeter-Kelvin"
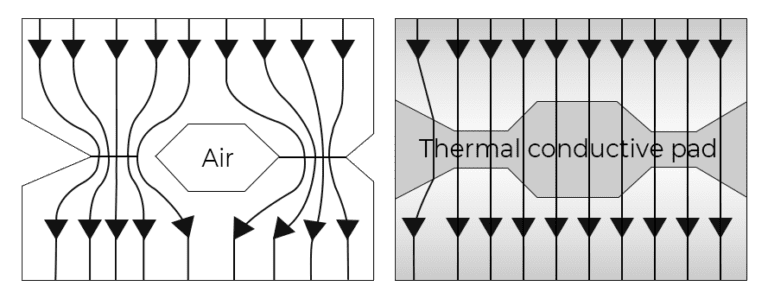
It's important to remember that thermal conductivity is a material (i.e., "bulk”or "intrinsic"') property and does not depend on the geometry of the test assembly. It simply describes the ability of a given material to transfer heat through internal heat conduction. Most critically, it does not account for any interfacial effects that may impede heat-flow, often to a significant degree.
If you would like to learn more about AOK performance thermal materials, please visit our website at www.aok-technologies.com.