As electronic devices continue to integrate more powerful functions into smaller components, temperature control has become one of the most critical challenges in the design, namely how to effectively take away the constraints of the architecture and the smaller and smaller operating space. More heat from a larger unit of power. Designers have been working to increase the CPU speed and processing power of various types of servers, which requires microprocessors to continuously improve thermal performance. But in other application areas, such as video game consoles, graphics equipment, and digital applications that require higher performance to support high-definition images, there is also a need for more computing power. As a result, chipmakers are focusing more than ever on thermally conductive materials and other technologies that can carry away excess heat that can adversely affect component stability and longevity. The operating temperature of the junction is known to have a dramatic effect on circuit (transistor) durability, and a small reduction in temperature (10°C ~ 15°C) can triple device life. Lower operating temperatures also reduce signal latency, which helps increase processing speed. In addition, lower temperatures reduce idle power dissipation (dissipated power) of the device, which reduces overall power dissipation.
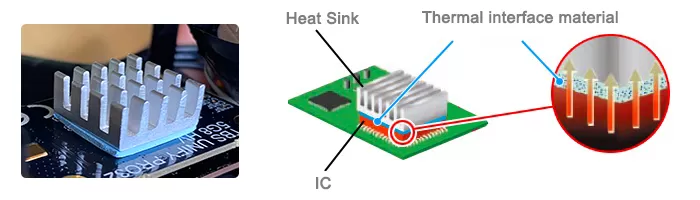
The thermal conductive sillcone pad has certain flexibility, excellent insulation, compressibility and natural viscosity on the surface. It is specially produced for the design scheme of using gaps to transfer heat. It can fill the gaps and complete the heat transfer between the heat-generating part and the heat-dissipating part. This kind of product It can be cut arbitrarily, which is conducive to automatic production and product maintenance. The process thickness of the silicone thermal insulation pad varies from 0.5mm ~ 5mm, and each 0.5mm is added, that is 0.5mm, 1mm, 1.5mm, 2mm ~ 5mm, and can be increased to 15mm for special requirements. It is specially produced for the design scheme of using gaps to transfer heat. Filling the gaps, completing the heat transfer between the heat-generating parts and the heat-dissipating parts, and also plays the role of shock absorption, insulation and sealing, which can meet the design requirements of the miniaturization and ultra-thinness of the company's equipment. It is a new material with great craftsmanship and usability. Widely used in electronic and electrical products.
Thermal paste is a new type of organic paste specially made for the heat transfer of electronic components. Good thermal conductivity and electrical insulation, shock absorption and impact resistance. Good use stability, low consistency and good construction performance, wide operating temperature range (-50℃ ~ +250℃, different models have different temperature ranges), heat-resistant, will not dry up under high temperature, Does not melt. It is non-corrosive to related materials, non-toxic, tasteless, and resistant to chemical corrosion. Outdoor use can avoid the adverse effects of ultraviolet light, ozone, moisture and chemicals.
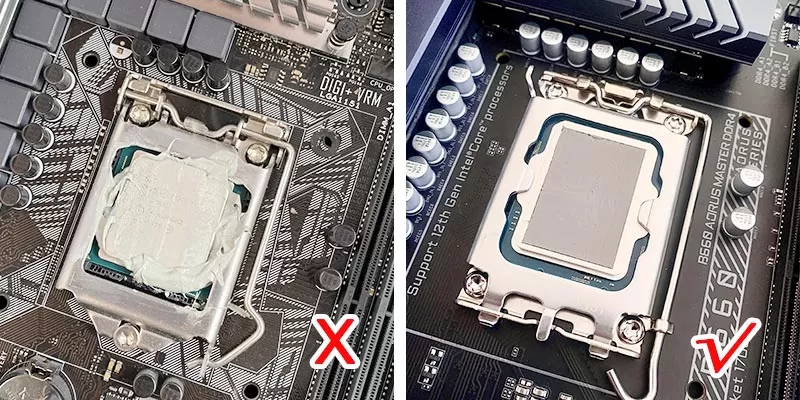
cpu thermal paste
• Thermal conductivity: The thermal conductivity of thermally conductive silicone pad and thermal conductive paste are 1.9W/m.K ~ 3.0W/m.K and 0.8W/m.K ~ 3.8W/m.K, respectively.
• Insulation: The thermal conductive silicone paste has poor insulation due to the addition of metal powder, and the thermal conductive silicone pad has good insulation performance. The electrical insulation index of 1mm thickness is above 4000v.
• Form: The thermal conductive paste is in the form of a paste, and the thermally conductive silicone pad is a sheet.
• Use: The thermal conductive silicone paste needs to be applied evenly (if it is large in size, it is more inconvenient to apply), it is easy to contaminate the surrounding devices and cause short circuits and scratch electronic components; the thermal conductive silicone pad can be arbitrarily cut, tear off the protective film and paste it directly , The tolerance is small, clean and save labor cost.
• Thickness: As a thermal conductive material for filling gaps, thermal conductive silicone paste is limited, and the thickness of thermal conductive silicone pad varies from 0.5mm ~ 10mm, which has a wide range of applications.
• Thermal effect: Thermal paste with the same thermal conductivity is better than soft silicone thermal sheet, because the thermal resistance of thermal paste is small. Therefore, to achieve the same thermal conductivity, the thermal conductivity of the thermally conductive silicone pad must be higher than that of the thermal conductive paste.
• Price: thermal conductive paste has been widely used, and the price is low. Thermally conductive silicone pads are mostly used in thin, small and precise electronic products such as notebook computers, and the price is slightly higher.
Type of Cooling Method | Pros | Cons |
| Thermal Paste | Spreads easily; Conforms to uneven surfaces; Fills large holes more evenly than pad; Better thermal conductivity when applied in a thin layer; Most pastes are less expensive than thermal pad. | Messy application process; Dries out; Can’t be reused. |
| Thermal Pad | Clean application; You can cut the pad to certain sizes to fit your specific setup; Can fill bigger holes. | More expensive than paste; Thicker material means less effective thermal conductivity |
AOK advice is to go with a thermal pad if you unsure how to apply thermal paste you should apply. If you're willing to perform the process, then a thermal paste is a better choice. Whichever you choose is a matter of your personal preference, as each method has advantages and disadvantages.
If you would like to learn more about AOK performance thermal materials, please visit our website at www.aok-technologies.com.
